GPU Compatibility with Motherboard – Complete Builder Guide!
Introduction
When building or upgrading a PC, understanding GPU compatibility with your motherboard is one of the most critical steps. A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) determines the system’s visual performance and graphical processing power, while the motherboard acts as the backbone that connects all components.
Ensuring that both the GPU and motherboard are compatible prevents hardware conflicts, underperformance, or even component failure. Compatibility issues can lead to poor frame rates, bottlenecks, or system instability — problems that can easily be avoided with proper planning.
What Does GPU and Motherboard Compatibility Mean?

Definition and Concept
GPU–motherboard compatibility refers to the ability of a graphics card to physically and electrically function with a motherboard. This includes alignment of PCI Express (PCIe) slot types, chipset support, and power delivery systems.
Role of PCIe Slots and Chipset
Most modern GPUs connect via PCIe x16 slots, found on nearly every contemporary motherboard. However, the PCIe generation (3.0, 4.0, or 5.0) influences bandwidth and performance. A PCIe 4.0 GPU will still work on a PCIe 3.0 motherboard, but with slightly lower data transfer speeds.
Overview of Physical and Power Connections
Apart from slot compatibility, the motherboard must also accommodate the GPU’s physical dimensions and provide sufficient power delivery through the PSU. Some high-end GPUs require dual or triple power connectors, which should be supported by your system’s power design.
Why GPU Compatibility Matters for Performance
Impact on Gaming and Rendering
GPU–motherboard compatibility directly affects rendering efficiency, frame rates, and thermal stability. If your motherboard doesn’t support the GPU’s full bandwidth potential, it can limit data transfer between the GPU and CPU, resulting in stuttering or lower FPS.
Bottleneck Issues Caused by Incompatible Setups
Even with a high-end GPU, pairing it with an outdated motherboard or CPU can cause a performance bottleneck. The GPU may process data faster than the motherboard or CPU can handle, leading to reduced performance efficiency.
Balancing GPU, CPU, and Motherboard
For optimal results, select a GPU that complements both your motherboard’s chipset and CPU’s capabilities. A balanced setup ensures the GPU operates at its full potential without overwhelming other system components.
Also read: CPU vs GPU Bottleneck
How to Check If Your GPU Is Compatible with Your Motherboard
Step-by-Step Compatibility Check Process
- Identify your motherboard model – Check your manual or use tools like CPU-Z.
- Check the PCIe slot – Confirm that the slot is PCIe x16 (Gen 3.0 or above).
- Compare GPU specifications – Ensure your GPU fits physically and electrically.
- Verify power requirements – Confirm PSU wattage and connector availability.
- Check BIOS updates – Some motherboards need firmware updates for newer GPUs.
Manufacturer Tools and Websites
Major GPU and motherboard manufacturers like ASUS, MSI, Gigabyte, and NVIDIA provide online compatibility lists that help match your GPU with your motherboard model.
Using Online Compatibility Checkers
Web-based tools such as PCPartPicker and BuildMyPC offer automatic compatibility validation by analyzing component databases.
Factors That Affect GPU and Motherboard Compatibility
PCIe Slot Type and Version
Modern GPUs use PCIe x16 slots. The difference between PCIe 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 lies in data transfer bandwidth — each new generation doubles the speed of the previous one. While cross-generation compatibility is maintained, using a newer GPU on an older PCIe slot slightly limits potential throughput.
Physical Size (GPU Length and Case Space)
Some GPUs, particularly high-end models like RTX 4080 or RX 7900 XTX, are significantly larger. Ensure your PC case has adequate clearance for length, width, and cooling airflow.
Power Supply Requirements
A GPU’s power draw varies depending on its model. A midrange card like an RTX 3060 may need a 550W PSU, while a high-end GPU like the RTX 4090 can require 850W or more. Always check for the right 8-pin or 16-pin connectors.
BIOS and Chipset Support

Older motherboards may need BIOS updates to recognize modern GPUs. Chipset series (e.g., Intel Z690 or AMD B650) influence PCIe generation and memory compatibility, both of which affect GPU performance.
CPU and RAM Limitations
If the CPU or RAM cannot keep up with the GPU’s processing power, you’ll face a CPU bottleneck, limiting overall output. Matching performance levels across all components ensures balanced processing efficiency.
Common Compatibility Questions
Can I Put Any GPU on a Motherboard?
Generally, yes — as long as the motherboard has a PCIe x16 slot. However, check for case space, PSU support, and BIOS compatibility.
What GPU Can My Motherboard Support?
Most motherboards support any modern GPU, but performance may vary depending on PCIe generation and CPU pairing.
Does It Matter What Motherboard You Have for a Graphics Card?
Yes. Higher-end motherboards provide faster PCIe lanes, better VRMs, and improved stability, which can impact GPU performance in high-load scenarios.
Are GPUs Universal to Motherboards?
Largely yes, since PCIe standards are backward compatible. Still, physical fit, power, and BIOS factors must be verified.
Motherboard/GPU Compatibility Explained
Understanding chipset families is key.
- Intel platforms (Z, B, and H series) differ in lane distribution and BIOS support.
- AMD platforms (X and B series) vary in PCIe generation and support for multi-GPU setups.
For example:
- Intel Z690 + RTX 4080 → full PCIe 5.0 bandwidth
- AMD B450 + RX 6700 XT → limited to PCIe 3.0 but still functional
Also read: GPU Memory Clock
Graphics Card and Motherboard Compatibility Checklist
Check for PCIe x16 slot availability
Verify power connectors and PSU wattage
Ensure physical space inside the case
Update motherboard BIOS if required
Review manufacturer compatibility lists
How to Find the Best Graphics Card for My Motherboard
When choosing the best GPU:
- Match PCIe generation (preferably 4.0 or higher).
- Ensure PSU and cooling support.
- Balance performance with CPU power.
Examples:
- Midrange builds: RTX 3060, RX 6700 XT
- High-end builds: RTX 4080, RX 7900 XTX
- Compact builds: RTX 4060, RX 7600 (for micro-ATX boards)
How Do I Know Which Graphics Cards Are Compatible?
Always check the manufacturer’s website for support lists and use tools like GPU-Z or PCPartPicker for compatibility confirmation. GPU comparison sites also allow side-by-side evaluation of size, TDP, and PCIe requirements.
Common Mistakes When Choosing a GPU for Your Motherboard
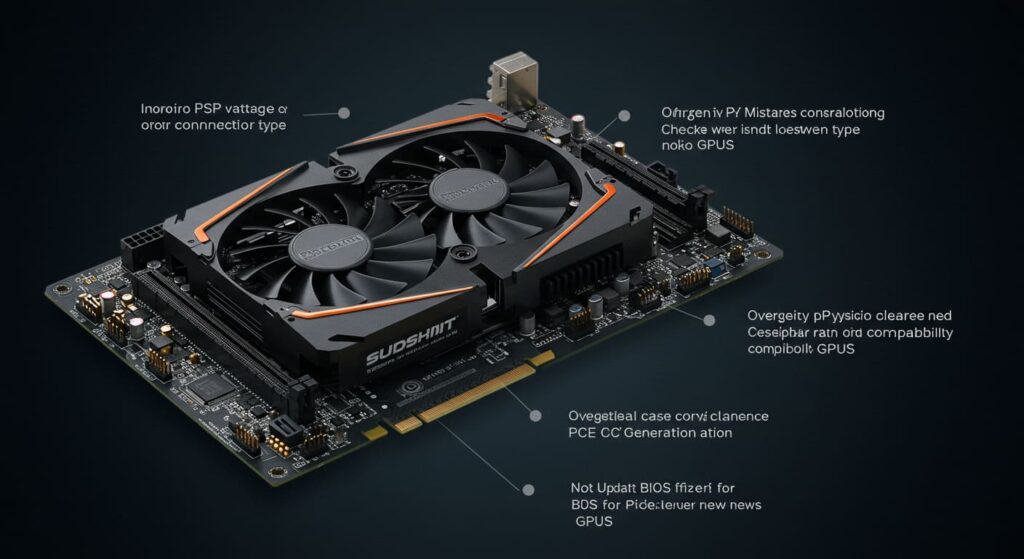

- Ignoring PSU wattage or connector type
- Forgetting to check physical case clearance
- Overlooking PCIe generation compatibility
- Not updating BIOS for newer GPUs
Avoiding these mistakes ensures seamless installation and optimal system efficiency.
GPU Compatibility with Motherboard Gaming
In gaming systems, motherboard choice affects how efficiently a GPU communicates with the CPU and RAM. For maximum gaming performance:
- Use motherboards with PCIe 4.0 or 5.0 lanes
- Enable Resizable BAR for improved GPU memory access
- Pair the GPU with a strong CPU to minimize latency and bottlenecks
Future-Proofing: Choosing a Motherboard for Next-Gen GPUs
The latest motherboards supporting PCIe 5.0 provide double the bandwidth of PCIe 4.0, making them ideal for next-generation GPUs. Investing in a PCIe 5.0-ready board ensures you won’t need a full system replacement when upgrading in the future.
FAQs About GPU Compatibility with Motherboards
1. How can I tell if my motherboard supports RTX GPUs?
Check for PCIe x16 slot availability and sufficient PSU wattage; RTX cards work on most modern boards.
2. Can I use a PCIe 4.0 GPU on a PCIe 3.0 motherboard?
Yes, but bandwidth will be limited to PCIe 3.0 speeds.
3. Do all motherboards support GDDR6 GPUs?
Yes — GDDR6 refers to GPU memory type, not motherboard RAM compatibility.
4. Will an RTX 3060 fit any motherboard?
As long as there’s a PCIe x16 slot and enough case space, yes.
5. How to know if my motherboard bottlenecks my GPU?
Monitor GPU usage; if it’s below 90% during heavy load, a CPU or motherboard bottleneck may exist.
6. Can BIOS updates fix GPU compatibility issues?
Yes. Manufacturers often release BIOS updates to support newer GPUs.
7. Is there a compatibility difference between AMD and NVIDIA GPUs?
No — both use the PCIe standard and are universally compatible.
8. Can I use multiple GPUs on one motherboard?
Only on boards that support SLI or CrossFire, and typically with high-end chipsets.
9. How much power does my motherboard need for a high-end GPU?
nsure your PSU provides at least 650–850W for high-end GPUs, depending on model.
10. What happens if my GPU isn’t fully compatible with my motherboard?
You may face boot errors, display issues, or the system might fail to detect the GPU altogether.
Conclusion:
Understanding GPU compatibility with your motherboard ensures you get the best possible performance from your PC. By checking PCIe slot versions, power requirements, BIOS support, and case dimensions, you can build a stable, efficient, and future-ready system.
Related post: